|
A to F G to M N to T U to Z |
Quadratic Equation A general quadratic equation is of the general form: ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b and c are constants and a 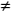 0. 0.
The values of x which satisfy the above equation are called the roots of the equation. They are found using this equation: 
b2 - 4ac is called the discriminant of the equation (symbol 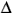 ). When: ). When:
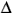 > 0, the roots will be real and different > 0, the roots will be real and different
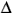 = 0, the roots will be real and equal = 0, the roots will be real and equal
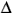 < 0, the roots will be complex < 0, the roots will be complex
The roots of a quadratic equation are denoted by the Greek letters 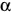 and and 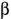 . The following can then be assumed: . The following can then be assumed:

and 
and the quadratic equation can then be re-written as:  . .
The following useful results can used when analysing roots of a quadratic:     . .
|
Top
[ H O M E ] [ S C I E N C E ] [ M A T H S ] [ A S T R O N O M Y ] [ S E A R C H ]
[ A to F ] [ G to M ] [ N to T ] [ U to Z ]
© 1997 - 1999, Jonathan Stott